ELECTROSCOPE |
Invented by the British physician William Gilbert around 1600, the electroscope is one of the most important instruments used by scientists for the past many years to study electricity.
What is an Electroscope?
An electroscope is a scientific device that is used to detect the presence of an electric charge on a body.
Working Principle of Electroscope
An electroscope is made up of a metal detector knob on top, which is connected to a pair of metal leaves hanging from the bottom of the connecting rod. When no charge is present, the metal leaves hang loosely downward. But, when an object with a charge is brought near an electroscope, one of the two things can happen.
- When the charge is positive, electrons in the metal of the electroscope are attracted to the charge and move upward out of the leaves. This results in the leaves having a temporary positive charge, and because like charges repel, the leaves separate. When the charge is removed, the electrons return to their original positions, and the leaves relax.
- When the charge is negative, the electrons in the metal of the electroscope repel and move toward the leaves on the bottom. This causes the leaves to gain a temporary negative charge, and because like charges repel, the leaves again separate. Then when the charge is removed, the electrons return to their original position, and the leaves relax.
An electroscope responds to the presence of a charge by moving electrons either into or away from the leaves. In both the above cases, the electrons will return to their original position, and the leaves will relax as soon as the charge is removed.
From all these statistics, we can conclude that the working of an electroscope is based on charge induction, the atomic and internal structure of the metal elements, and the notion that unlike charges attract while charges repel each other. Moreover, the electroscope cannot identify whether the charge is positive or negative; rather, it only determines the presence of the charge.
![]()
Types of Electroscope
There are two types of electroscopes as follows :
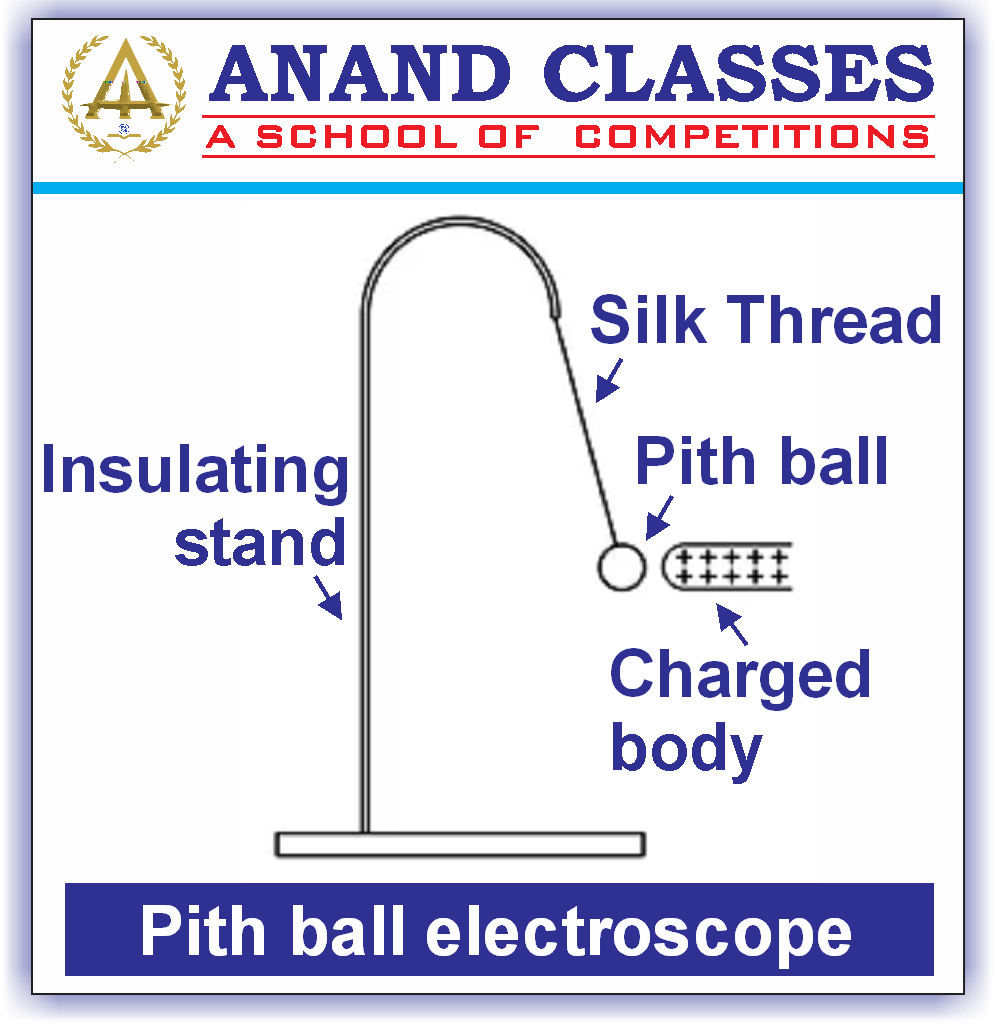
Pith-ball electroscope : Pith-ball electroscope was invented by John Canton in the year 1754. It consists of one or two small balls that are made up of a lightweight non-conductive substance and known as pith. To determine whether the object is charged or not by using this electroscope, the object is brought close to the uncharged pith-ball. The force of attraction between the ball and object shows that the object is charged.
 Gold-leaf electroscope : Gold-leaf electroscope was developed by Abraham Bennet in the year 1787, which is more sensitive than pith-ball electroscope. It consists of two gold leaves and is used for detecting the electrical charge of the body and for the classification of its polarity.
Gold-leaf electroscope : Gold-leaf electroscope was developed by Abraham Bennet in the year 1787, which is more sensitive than pith-ball electroscope. It consists of two gold leaves and is used for detecting the electrical charge of the body and for the classification of its polarity.
GOLD LEAF ELECTROSCOPE |
The gold leaf electroscope is a sensitive electroscope type that is used for detecting charges.
It consists of a brass rod with a brass disk at the top, and at the bottom, there are two thin gold leaves in the form of foils.
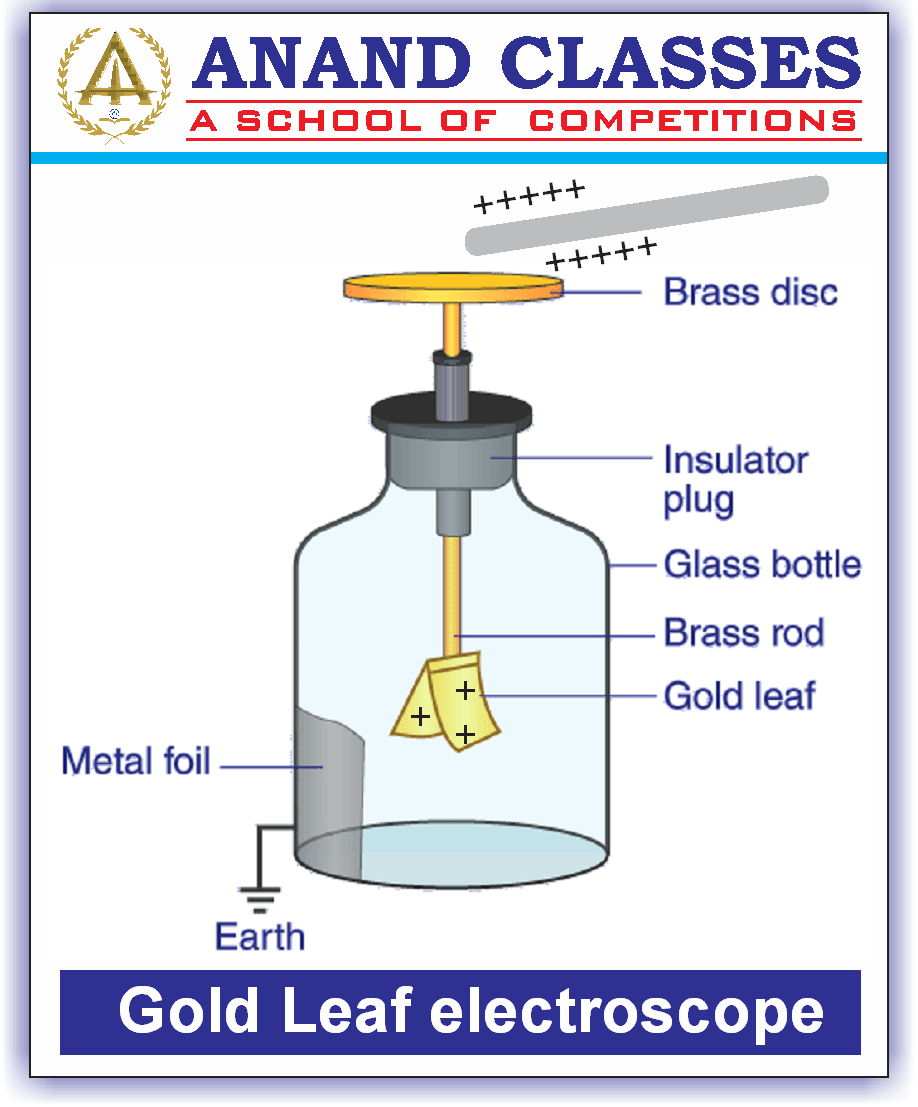
In order to keep the rod in place, the rod travels through the insulator. The charges move from the disk to the leaves through the rod. At the lower portion of the jar, a thin aluminium foil is connected. The aluminium foil is grounded with the help of a copper wire so that the leaves are protected from external electrical disruptions.
![]()
Applications of Gold Leaf Electroscope
The following are the applications of gold leaf electroscope:
Detect Charge
For the detection of charge, the object that needs to be tested is touched with the metal cap. If the leaves diverge, the body is said to be charged, and if there is no change in the leaves of the electroscope, then the body is uncharged.
Identification of the Nature of the Charge
To identify the nature of the charge, let’s consider an example. A positively charged body is brought near the metal cap. Then an unknown body is brought near the metal cap. If the leaves diverge further, we can conclude that the unknown body has a positive charge. If the leaves come closer to each other, then the charge of the unknown body is negative.
Identification of Body as a Conductor or an Insulator
To identify if a body is a conductor or an insulator, two gold leaf electroscopes are taken. One gold leaf electroscope is charged so that the leaves will diverge. Then the other gold leaf electroscope is connected to the first one. If the leaves of the other electroscope diverge, then the body is said to be a conductor, and if there is no change in the leaves, the body is said to be an insulator.
![]()
Uses of electroscope
Following are the uses of electroscope:
- It is used to detect the static charges
- The nature of electric charges can be determined using an electroscope
- The magnitudes of two different charges can be compared using an electroscope
![]()
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is an electroscope?
An electroscope is a device used to detect the presence of an electric charge on a body.
What is an electrometer?
An electrometer is an instrument used to measure the charge quantitatively.
What are the types of electroscopes?
Types of electroscopes are:
- Pith-ball electroscope
- Gold-leaf electroscope
Who developed the gold-leaf electroscope?
In the year 1787, the Gold-leaf electroscope was developed by Abraham Bennet.
What is the name of the first electroscope?
The name of the first electroscope is Versorium. This was a pivoted needle-like electroscope invented by William Gilbert, who was a British physicist, in the year 1600.
Why is a gold leaf electroscope enclosed in a glass case?
A gold leaf electroscope is enclosed in a glass case so that the gold leaves are protected from the air. This also helps in capturing the charge leak through the air so that the sensitivity of the instrument can be increased.
What does the degree of divergence of gold leaves mean in a gold leaf electroscope?
The degree of divergence of gold leaves in a gold leaf electroscope is an indicator of the amount of charge that is transferred to the gold leaves.
Why do the gold leaves in an electroscope fold back when touched with hands?
The gold leaves in an electroscope fold back when they are touched with hands because the charge is earthed.
What are the three methods for charging objects?
The 3 methods for charging objects are friction, conduction, and induction.
State true or false: Electroscope is used to detect the static charges.
True.


































